SNMP Event Monitor Reference Guide
SNMP Event Monitor
Monitors SNMP networking gears' various values.
Overview
The SNMP Event Monitor can watch any value supported by your networking gear and other equipment that supports SNMP. It has a wide variety of options supporting SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3. To select the items to monitor, you can use either the numeric OID for the value or (if the matching MIBs are present) a symbolic name.
As an example, to monitor system uptime you can use the standard symbolic name "system.sysUpTime.0", or you can use the equivalent numeric OID which is ".1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0". The numeric OIDs are not as easy for end users to interpret but using numeric OIDs allows the event monitor to use high-performance techniques to gather the SNMP values. As a result, we recommend that you use numeric OIDs whenever possible, especially if your monitoring configuration uses SNMP extensively.
If you prefer to use symbolic names, the appropriate MIBs must be present in the MIBs subfolder under the main FrameFlow installation folder. MIBs are text files that help our SNMP engine to translate symbolic names into numerical OIDs. FrameFlow ships with a set of commonly used MIB files. To add new MIBs, download them from the manufacturer's website and copy them to FrameFlow's MIBs subfolder.
Use Cases
- Monitoring custom SNMP values on your networking equipment
Monitoring Options
This event monitor provides the following options:
SNMP Version
Select the SNMP version that will be used to collect the inventory data. The best version to use will depend on how your network devices have been configured. Most devices support SNMPv1, but some may require SNMPv2 or SNMPv3.
Community
Enter the SNMP community string that will be used to connect. The community string is equivalent to a password. The default community string for read-only access is "public" so use this value if you are unsure of what community string your devices are configured to use. The community string is only required for SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c connections. SNMPv3 uses different authentication parameters.
Port Number
The standard port number for SNMP requests is 161. If your devices have been configured to use a different port you can specify it here.
Timeout
The timeout tells the event monitor how long to wait for a response. The default value is best for almost all situations but you can increase or decrease it if you choose.
Retries
Since SNMP runs on UDP, packet delivery and response are not guaranteed. For this reason, it is good practice to tell the event monitor to retry one or more times if it does not receive a response.
Username (SNMPv3 Only)
Specify the user name that will be used when connecting to the network device. This is a required value for the SNMPv3 protocol.
Context (SNMPv3 Only)
In rare cases, a context string is required to establish the SNMPv3 connection. If required by your devices, enter it here. This value is optional.
Security Level (SNMPv3 Only)
SNMPv3 connections can support both authentication and privacy. Authentication means that a valid passphrase must be supplied or the SNMP unit will not accept the connection. Privacy means that the connection to the SNMP device must be encrypted otherwise the device will not accept it. Both are optional. If your devices do not require either, select noAuthNoPriv. If your devices require authentication but not privacy, select authNoPriv. If your devices require both authentication and privacy, select authPriv.
Auth. Protocol Level (SNMPv3 Only)
If authNoPriv or authPriv is selected for the security level, you must specify the authentication protocol for the connection. Supported values are MD5, SHA, SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512. Consult the documentation and configuration of your network devices to determine which protocol they support.
Auth. Passphrase (SNMPv3 Only)
Enter the authentication passphrase that your SNMP devices have been configured to accept. This value is required when authNoPriv or authPriv is selected for the security level.
Privacy Protocol (SNMPv3 Only)
If authPriv is selected for the security level, the privacy protocol must be selected. The supported values are DES and AES.
Priv. Passphrase (SNMPv3 Only)
Enter the privacy passphrase that your SNMP devices have been configured to accept. This value is required when authPriv is selected for the security level.
Items to Monitor
OID/Symbolic Name - Enter the numeric OIDs or symbolic names of the SNMP values that you want to monitor. For high-volume monitoring, we recommend using the numeric OID whenever possible. FrameFlow's monitoring engine can directly use numeric OIDs which saves on look up times.
- Label (Optional) - Enter a friendly name for the OID or symbolic name. The label will be used in all alerts and notifications instead of the OID or symbolic name. For example, choosing the label "Uptime" for ".1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0" will make it more clear what the value represents.
- Level - Select alert level for events that are generated when the detected value does not pass the comparison type.
- Comparison - What test the event monitor will use for the detected value. The value can be interpreted as a string or as a numeric value.
- Value - Select what the detected item will be compared with. For example, the event monitor will alert when the comparison is "Alert if greater than (Number)" and the comparison value is 10 and the detected value is 11.
- Data Type - Select the data type that best matches the value you are monitoring. The data type will determine how the value is formatted in notifications and displayed in graphs.
- Scale (Optional) - For numeric values, you can specify a scale. The event monitor will multiply the detected value by the scale value and use the result in all alerts, notifications, and graphs.
- Postfix (Optional) - The postfix is a text value that will be added to the end of the value when it is displayed in alerts and notifications. For example if the value being monitored is a temperature then you might specify a postfix of " degrees" or "F" or "C".
Monitoring SNMP Tables
To monitor SNMP tables, specify the OID or symbolic name of a table item that you want to monitor and append ".*" to it.
For example, to monitor the ifSpeed item of the MIB-II ifEntry table, use: RFC1213-MIB::ifSpeed.*
By default, the same label will be applied to each item in the table but for additional clarity, you can tell the event monitor to use a different table item as the label. To do this, edit the label field and include the table item to be used for labels in between two pairs of percent signs.
For example: %%RFC1213-MIB::ifDescr.*%%
That will tell the event monitor to first retrieve the value for each ifSpeed entry and use the corresponding ifDescr items as labels. You can add extra text before or after the label items specifier. For example: Interface %%RFC1213-MIB::ifDescr.*%%
Authentication and Security
For SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c, a community string for the device being monitored is required. For SNMPv3, a username and other SNMPv3 parameters are required.
Protocols
Data Points
This event monitor will generate one data point for each item in the "Items to Monitor" section and each item in the calculation section.
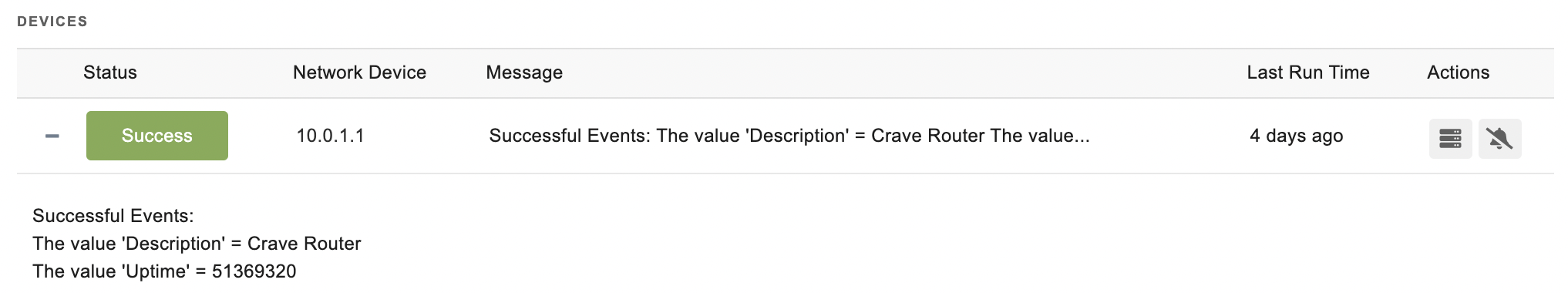
Sample Output
Tutorial
To view the tutorial for this event monitor, click here.
Comments
Add a comment