Day 24: Security Best Practices
30 Days of FrameFlow
FrameFlow's Security Best Practices
Today, we'll show you how to configure some advanced security settings so you'll be set up with optimal security should you proceed with FrameFlow after your free trial. Instructional information is available in our Technical Resources and as a PDF.
If you haven't yet done so, this is a good time to start running FrameFlow on IIS. Complete instructions on how to do so are found here.
Security Roles
FrameFlow's Login and Security settings let you designate security roles based on the minimum amount of clearance each user needs. Setting things up this way optimizes security as the most important administrative actions can be done only by those with the highest clearance. Give new users and roles the lowest possible security clearances for their purposes each time.
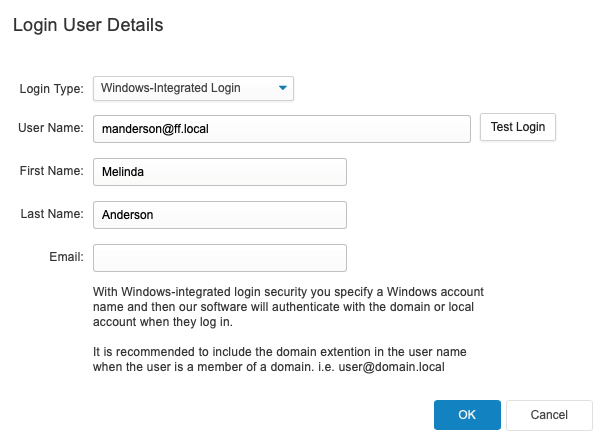
Windows Integrated Security
In the login user details for each FrameFlow user, there's a selection of login types to choose from. By default, your FrameFlow logins will be of the "Standard" type, which means that FrameFlow only requires a correct username and password and doesn't authenticate with a third party before letting you in. We recommend changing the login type for each of your users to use Windows Integrated Security, which links your FrameFlow logins to your Windows domain or local account.
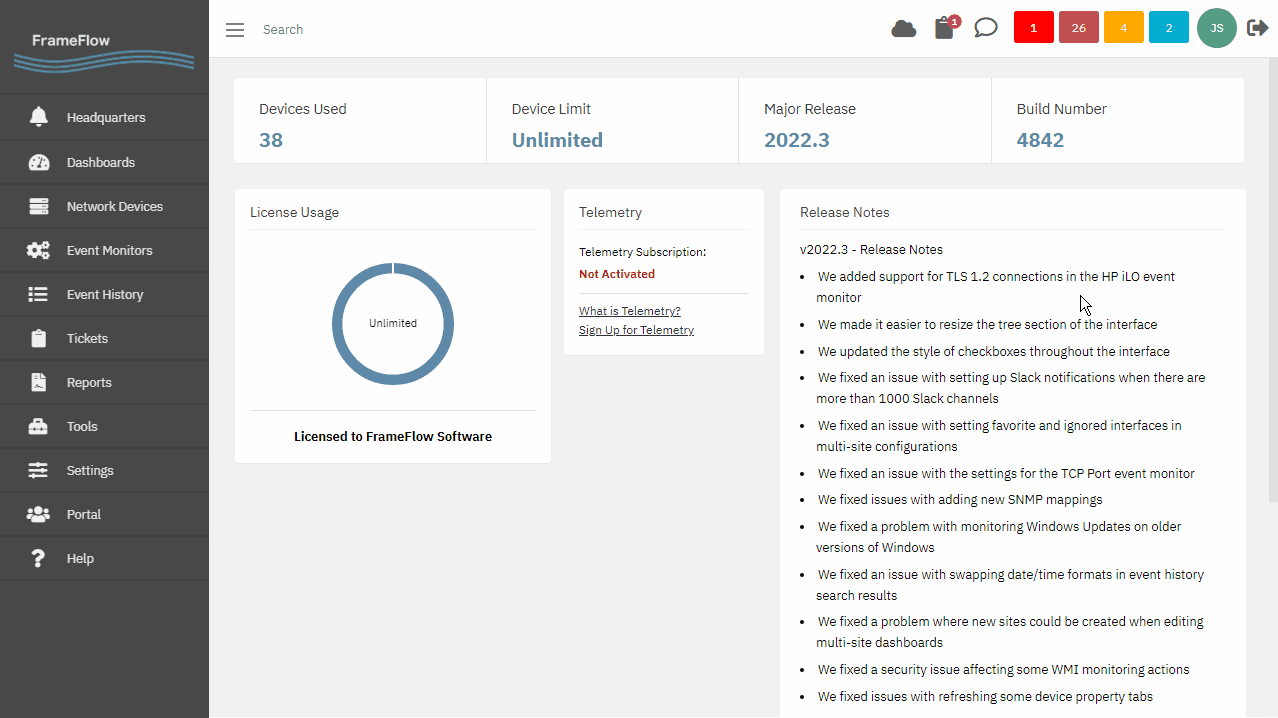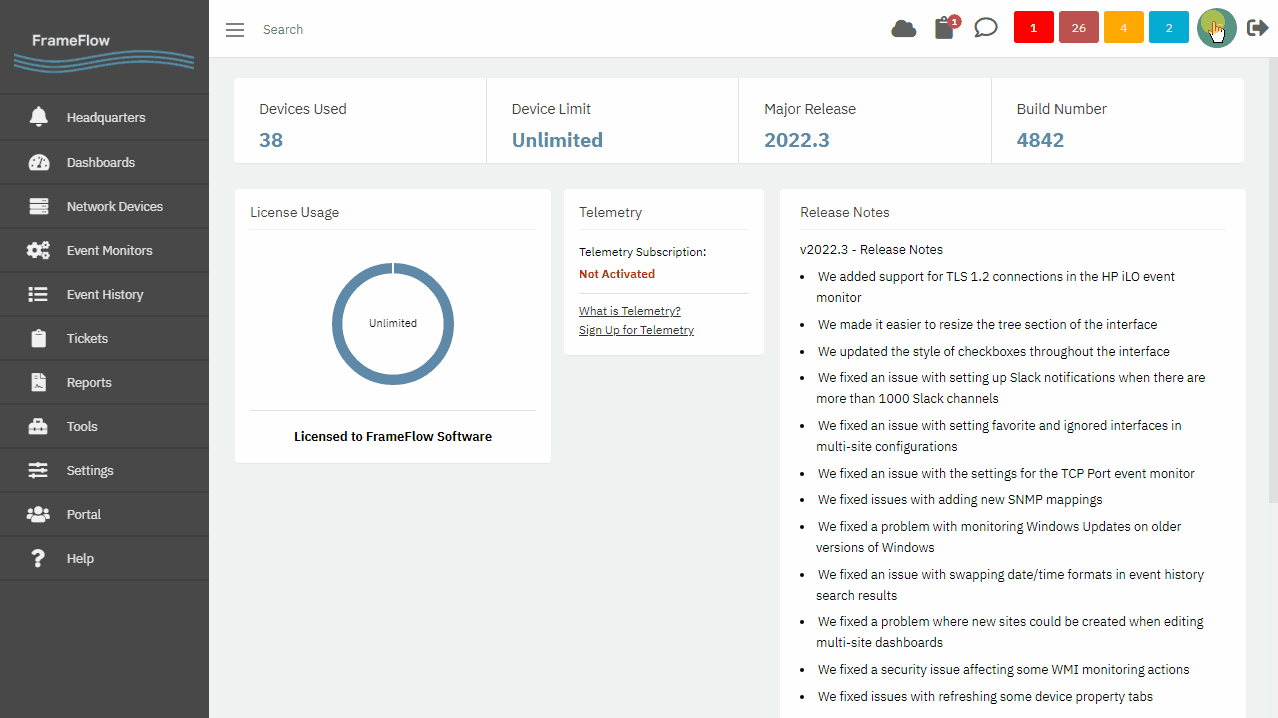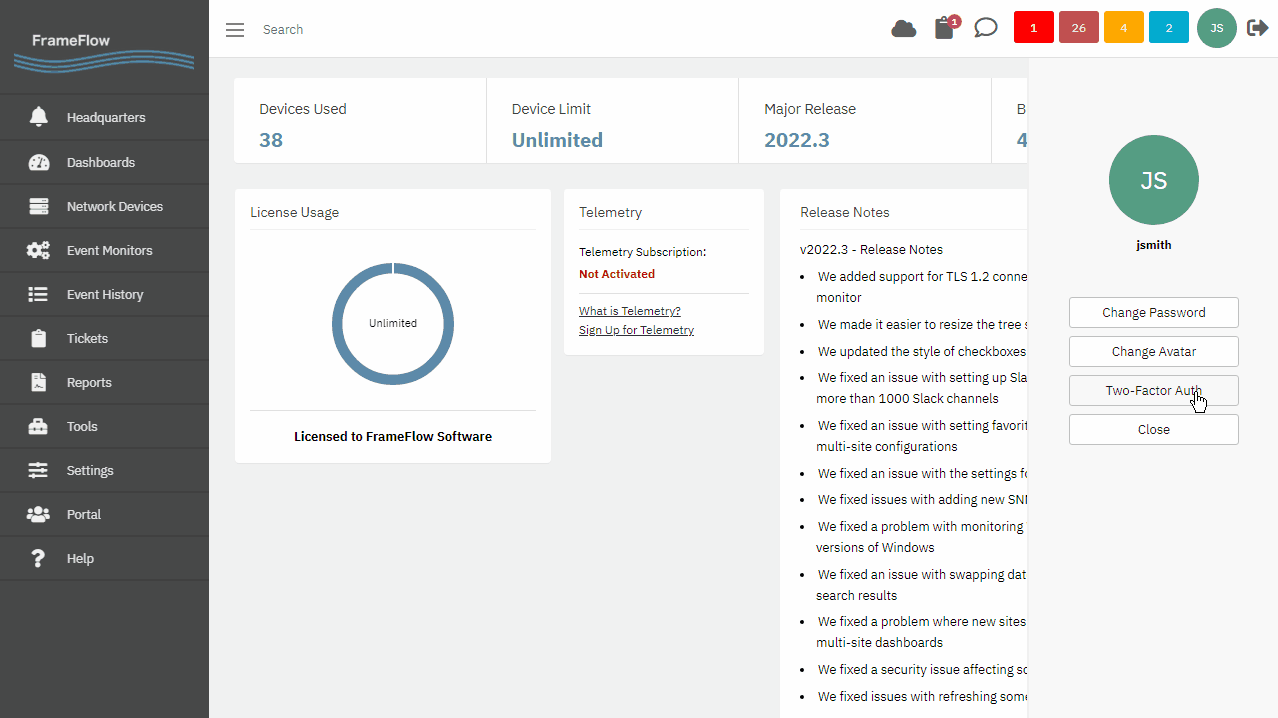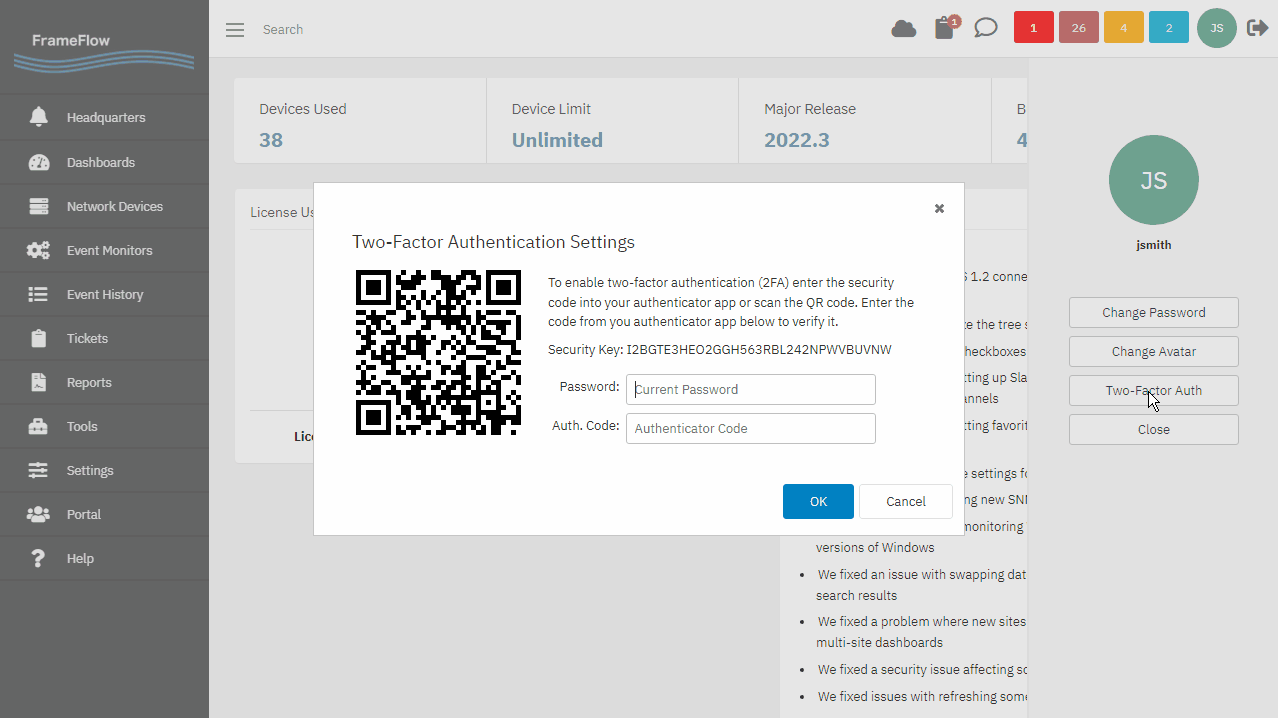
Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication is another popular security-enhancing method that FrameFlow supports. Enabling two-factor authentication adds a second layer of verification and security to your FrameFlow accounts by linking your accounts to your employees' phones. We have an article about enabling two-factor authentication in our Features section.
Summary
To learn more about the steps you can take to achieve maximum security with your FrameFlow installation, please check out our Security Best Practices guide. There, you can find high-security tips for multi-site configurations as well. The Security Best Practices guide also details how to control inbound and outbound access to your FrameFlow master console and remote nodes. Make sure to tune in tomorrow when we dive into database monitoring with FrameFlow!
| Day 23: Device Types | Day 25: Database Monitoring |
Table of Contents
Back to Menu
Day 1: Intro and Installation
Day 2: FrameFlow's Interface
Day 3: Network Devices
Day 4: Your First Event Monitors
Day 5: Authentication Profiles
Day 6: Security
Day 7: System Health Event Monitor
Day 8: Event Monitors by Category
Day 9: Headquarters
Day 10: Dashboards
Day 11: Alert Types
Day 12: PowerShell Scripting
Day 13: Event History
Day 14: Reports and Inventory Monitoring
Day 15: Network Monitoring
Day 16: Cloud Service Monitoring
Day 17: Cloud Cost Monitoring
Day 18: Activity Monitoring
Day 19: Maintenance Windows
Day 20: Dependencies
Day 21: VMware Monitoring
Day 22: Benefits of Organization
Day 23: Assigning Device Types
Day 24: Security Best Practices
Day 25: Database Monitoring
Day 26: Hardware Monitoring
Day 27: Installation Health Event Monitor
Day 28: Multi-Site and Remote Nodes
Day 29: Failover Monitoring
Day 30: More FrameFlow Resources